Join our community to see how developers are using Workik AI everyday.
Supported AI models on Workik
GPT 5.2 Codex, GPT 5.2, GPT 5.1 Codex, GPT 5.1, GPT 5 Mini, GPT 5
Gemini 3.1 Pro, Gemini 3 Flash, Gemini 3 Pro, Gemini 2.5 Pro
Claude 4.6 sonnet, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, Claude 4.5 Haiku, Claude 4 Sonnet
Deepseek Reasoner, Deepseek Chat, Deepseek R1(High)
Grok 4.1 Fast, Grok 4, Grok Code Fast 1
Models availability might vary based on your plan on Workik
Features

Generate Docstrings Automatically
AI generates Pythonic docstrings instantly using function signatures, type hints, decorators, and inferred behavior.

Map Classes and Methods
AI uses class hierarchies, inherited methods, mixins, and overridden logic to produce clean, well-structured documentation.

Analyze Your Entire Codebase
AI analyzes repositories & generates consistent documentation across utilities, scripts, services, and shared modules.

Extract Logical Flows Clearly
Get explanation for complex logic blocks, branches, conditions, and loops to clarify execution paths and side effects.
How it works
Create your account instantly using Google or manually sign up to begin generating documentation.
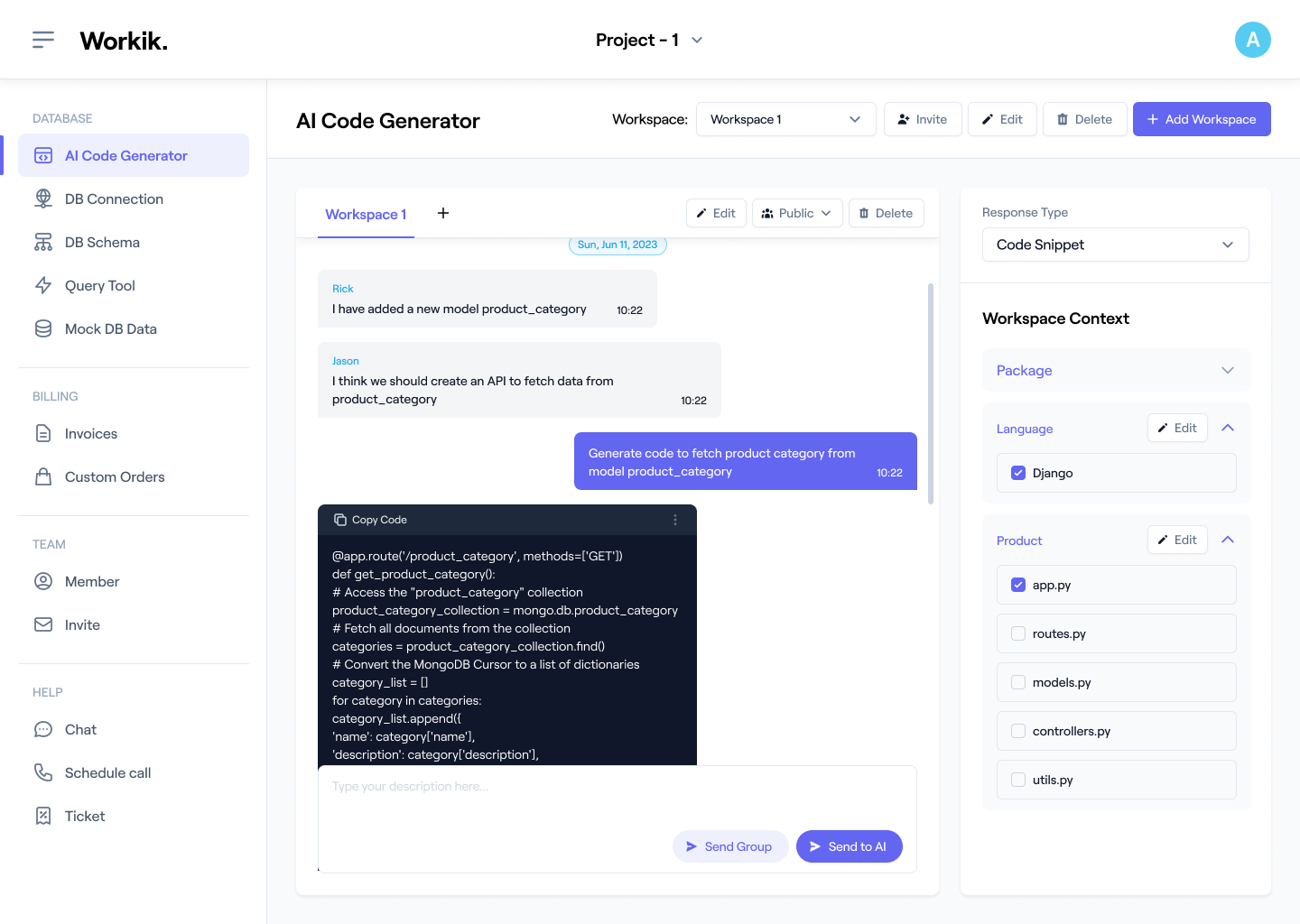
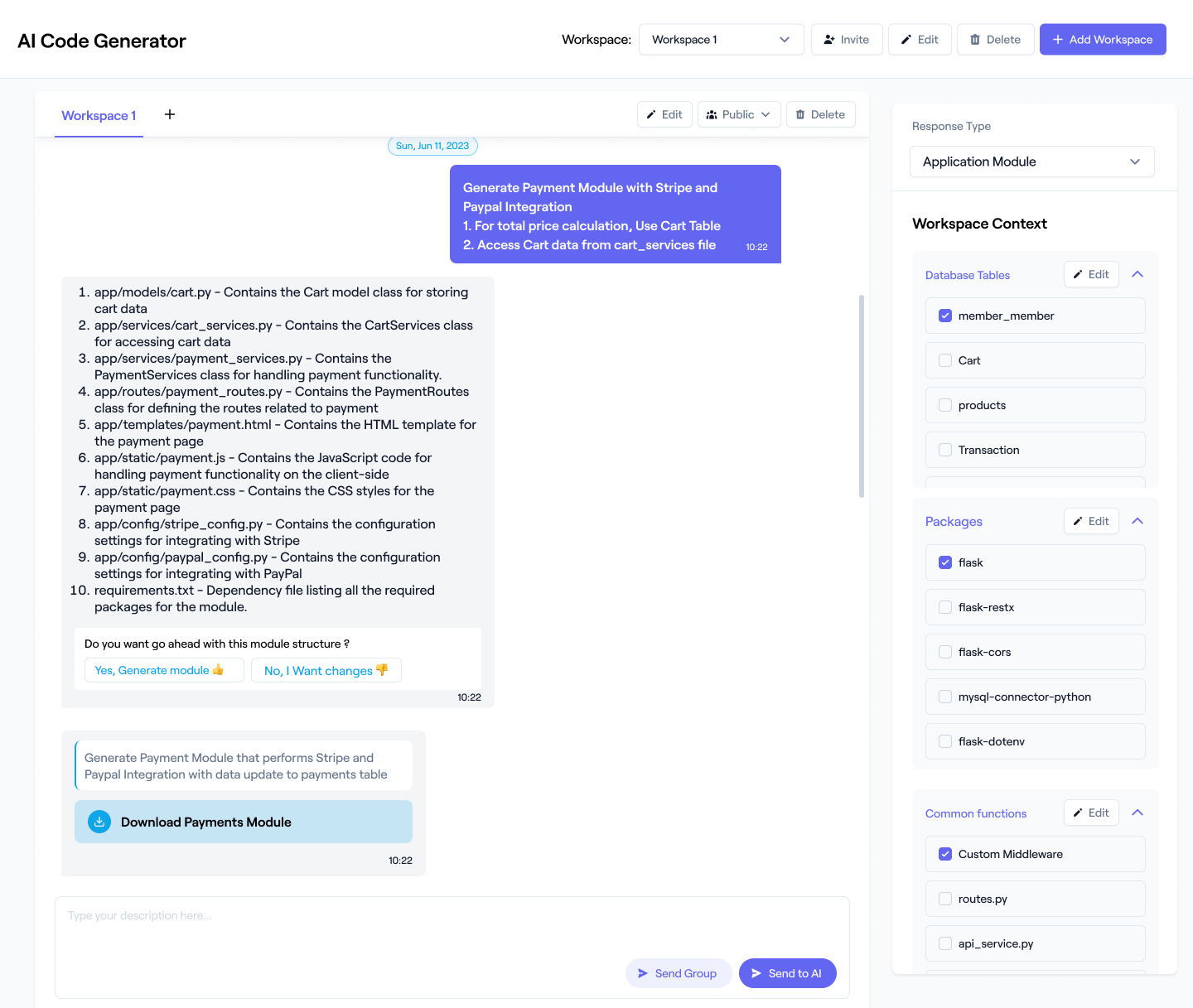
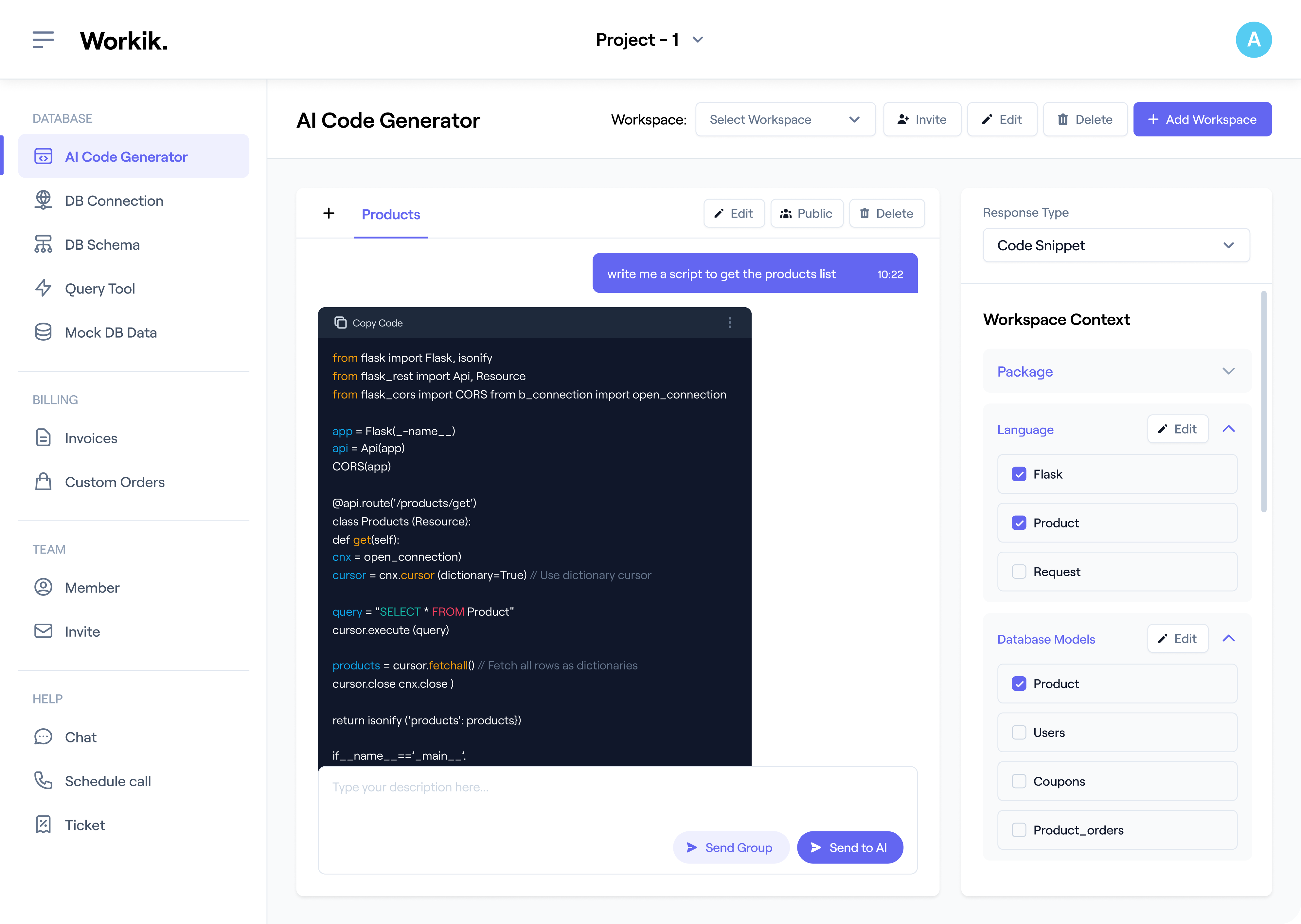
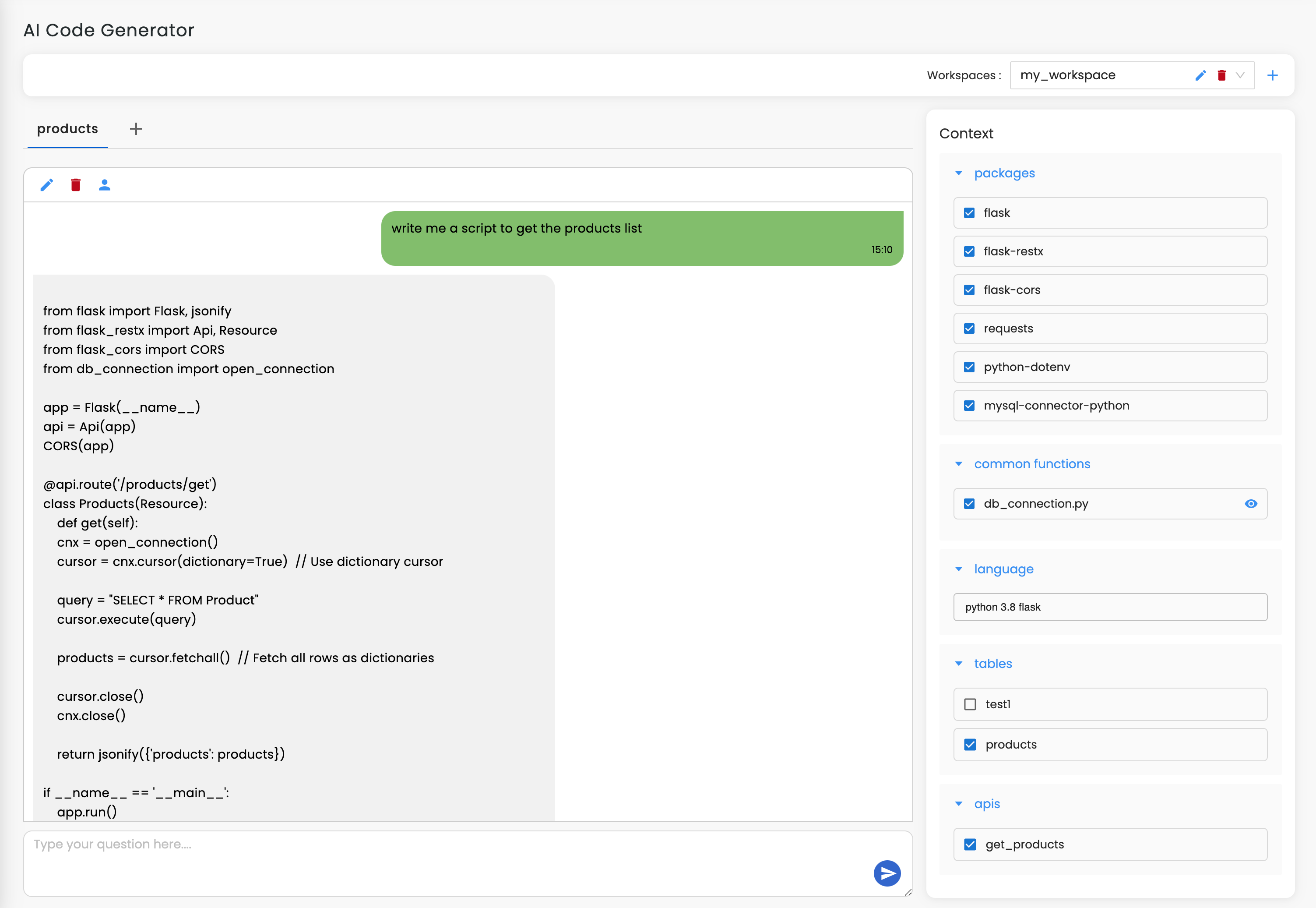
Workik provides specific feature sets for code documentation. Add Python code files or connect repositories from GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps for full codebase analysis. Users can specify their preferred docstring style, such as Google, NumPy, or reStructuredText (rST), to ensure the AI generates consistent documentation.
Use AI to generate Python docstrings, explain logic flows, map class structures, produce module summaries, or document entire repositories based on the context you provide and the layout that you prefer.
Invite teammates to share and refine generated documentation within Workik. Continue expanding coverage across modules, classes, and APIs using AI-powered follow-up tasks.

Expand

Expand

Expand

Expand

Expand


Expand


Expand


TESTIMONIALS
Real Stories, Real Results with Workik
"Workik Chat With AI feature explained complex Python logic instantly. It’s like having a senior dev beside me."
.png)
Akitoshi Lee
Junior Developer
"Workik AI generated clean docs for our ML pipelines straight from notebooks and scripts."
.png)
Maria Petrova
Machine Learning Engineer
"Our monorepo finally has consistent reliable documentation thanks to Workik AI’s codebase-wide analysis."
.png)
Landon Carter
Engineering Manager
What are the most common use cases of Workik’s Python Code Documentation Generator for developers?


Developers use Workik for a wide range of Python documentation tasks, including but not limited to:
* Auto-generating docstrings for functions, classes, and modules using signatures and type hints.
* Explaining complex logic blocks, branching conditions, and multi-step algorithms.
* Documenting Django/Flask/FastAPI endpoints directly from route decorators and serializers.
* Summarizing entire repositories to create project overviews and architectural documentation.
* Extracting clear explanations from Jupyter notebooks and ML pipeline scripts.
* Generating API reference docs for internal SDKs, utilities, and shared libraries.
* Converting inline comments into structured documentation that follows consistent style standards.
* Documenting data transformations, ETL processes, and Pandas/Numpy workflows for DS/ML teams.
What context-setting options are available when generating Python documentation with Workik?


While context-setting is optional, adding it helps personalize and sharpen AI-generated documentation. Developers can provide:
* Direct repo integration via GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket for automated context sync
* Python files, folders, or entire repos for deeper code understanding
* Docstring style preferences (Google, NumPy, or reStructuredText)
* Dynamic notes describing project rules, naming conventions, or architectural context
Can AI generate documentation for large or legacy Python codebases with minimal or outdated comments?


Yes. AI can analyze legacy or comment-poor Python codebases by reading control flow, import chains, naming patterns, and function signatures. It then produces complete documentation—module summaries, function descriptions, class overviews—without requiring refactoring or rewrites. This is ideal for inherited enterprise repos, old utility scripts, or long-neglected internal tools.
Can the AI document Python notebooks and ML/DS pipelines?


Yes. AI can read .ipynb notebooks, extract critical code cells, interpret data transformations, outline ETL steps, and document ML pipelines end-to-end. It turns exploratory notebooks into structured documentation, useful for ML teams needing reproducibility and clarity.
How well can AI handle documenting complex Python OOP structures?


AI can document multi-level inheritance, overridden methods, mixins, ABCs, data classes, and dunder methods. It explains class responsibilities, relationships, lifecycle logic, and method behavior—making even deeply nested OOP codebases easier to understand and maintain.
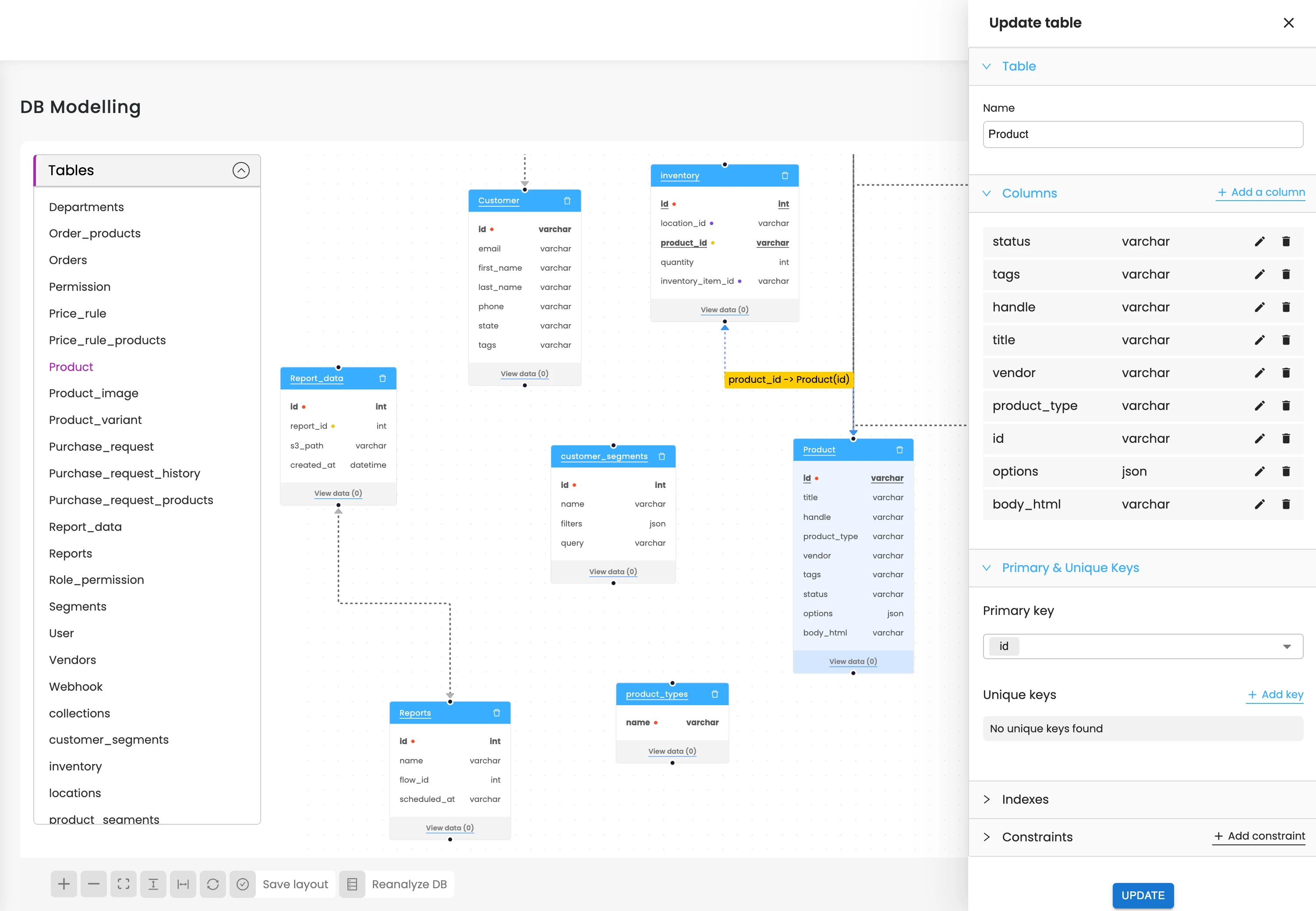
Can the AI generate architecture-level documentation for Python projects?


AI analyzes folder structures, logical import relationships, module interactions, service boundaries, and shared utilities to generate architecture overviews. This includes explaining how components communicate, how data flows across layers, and how responsibilities are distributed across the project.
Can AI detect missing documentation and help standardize docstring styles across the project?


Yes. AI flags undocumented functions, mismatched parameter descriptions, outdated docstrings, and inconsistent documentation styles. It can standardize everything into a single format Google, NumPy, or rST, ensuring cohesive Python documentation across contributors and versions.
Can the tool maintain versioned documentation across branches or releases?


Yes. With repo integration, the AI can generate or update documentation per branch, tag, or release. This is ideal for teams maintaining LTS branches, releasing incremental API updates, or supporting multiple major versions of a Python package.
Generate Code For Free

Python Code Documentation Question & Answer
Python Code Documentation refers to the structured explanation of Python modules, functions, classes, APIs, and code behavior through docstrings, reference guides, architecture summaries, and usage examples. It helps developers understand intent, logic flow, dependencies, edge cases, and best practices.
Common languages, frameworks, and execution models documented in Python systems include:
Language Core:
Python with dynamic typing, duck typing, decorators, generators, and context managers
Web Frameworks:
Django, FastAPI, Flask
Application Types:
Web backends, REST APIs, CLI tools, automation scripts, background workers
Async & Concurrency Models:
asyncio, async/await, thread pools, multiprocessing
Data & ML Ecosystem:
NumPy, Pandas, scikit-learn, PyTorch
Notebook & Research Workflows:
Jupyter Notebook, experiment-driven pipelines
Packaging & Structure:
Modules, packages, virtual environments, dependency graphs
Common use cases for Python Code Documentation include:
Docstring Clarity:
Explaining function purpose, parameters, return values, raised exceptions, and side effects.
API Documentation:
Describing endpoint behavior, request/response models, validation rules, and auth flows.
Data & ML Reproducibility:
Documenting preprocessing steps, feature pipelines, model logic, and evaluation flows.
Async Flow Understanding:
Clarifying async functions, background tasks, concurrency boundaries, and I/O behavior.
Large Codebase Onboarding:
Helping developers navigate multi-module Python repositories quickly.
Notebook Interpretation:
Turning exploratory notebooks into readable, reproducible artifacts.
Library & SDK Usage:
Documenting reusable utilities, internal packages, and shared abstractions.
Error & Edge-Case Visibility:
Capturing failure modes, fallback logic, and expected misuse scenarios.
Workik AI is optimized for Python’s dynamic and convention-heavy nature, including:
Docstring Generation:
Produces clear Google, NumPy, or rST-style docstrings from real code behavior.
Function & Class Explanation:
Explains decorators, generators, dunder methods, and dynamic patterns.
API Documentation:
Documents FastAPI routes, Django REST views, Flask endpoints, and schemas.
Notebook & ML Context:
Extracts structure and intent from notebooks, ETL scripts, and model pipelines.
Repository Summaries:
Generates module-level overviews and dependency explanations.
Async & Flow Breakdown:
Clarifies async routines, background workers, and concurrency boundaries.
Documentation Cleanup:
Detects missing or outdated docstrings and standardizes style.
Version-Aware Docs:
Keeps documentation aligned across branches, releases, and evolving APIs.
Explore more on Workik
Top Blogs on Workik
Get in touch
Don't miss any updates of our product.
© Workik Inc. 2026 All rights reserved.

