Join our community to see how developers are using Workik AI everyday.
Supported AI models on Workik
GPT 5.2 Codex, GPT 5.2, GPT 5.1 Codex, GPT 5.1, GPT 5 Mini, GPT 5
Gemini 3.1 Pro, Gemini 3 Flash, Gemini 3 Pro, Gemini 2.5 Pro
Claude 4.6 sonnet, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, Claude 4.5 Haiku, Claude 4 Sonnet
Deepseek Reasoner, Deepseek Chat, Deepseek R1(High)
Grok 4.1 Fast, Grok 4, Grok Code Fast 1
Models availability might vary based on your plan on Workik
Features

Document Schema Structure
AI documents tables, columns, data types, and constraints for complete, reliable MS-SQL schema clarity.

Map Database Relationships
AI maps foreign keys and dependencies so developers can understand table relationships safely.

Explain Stored Logic
Stored procedures, functions, & triggers are broken down by AI to show inputs, outputs, & affected tables.

Clarify Indexes & Constraints
AI documents indexes, primary keys, and constraints while explaining their impact on queries and performance.
How it works
Create your Workik workspace in seconds using manual signup or Google login.
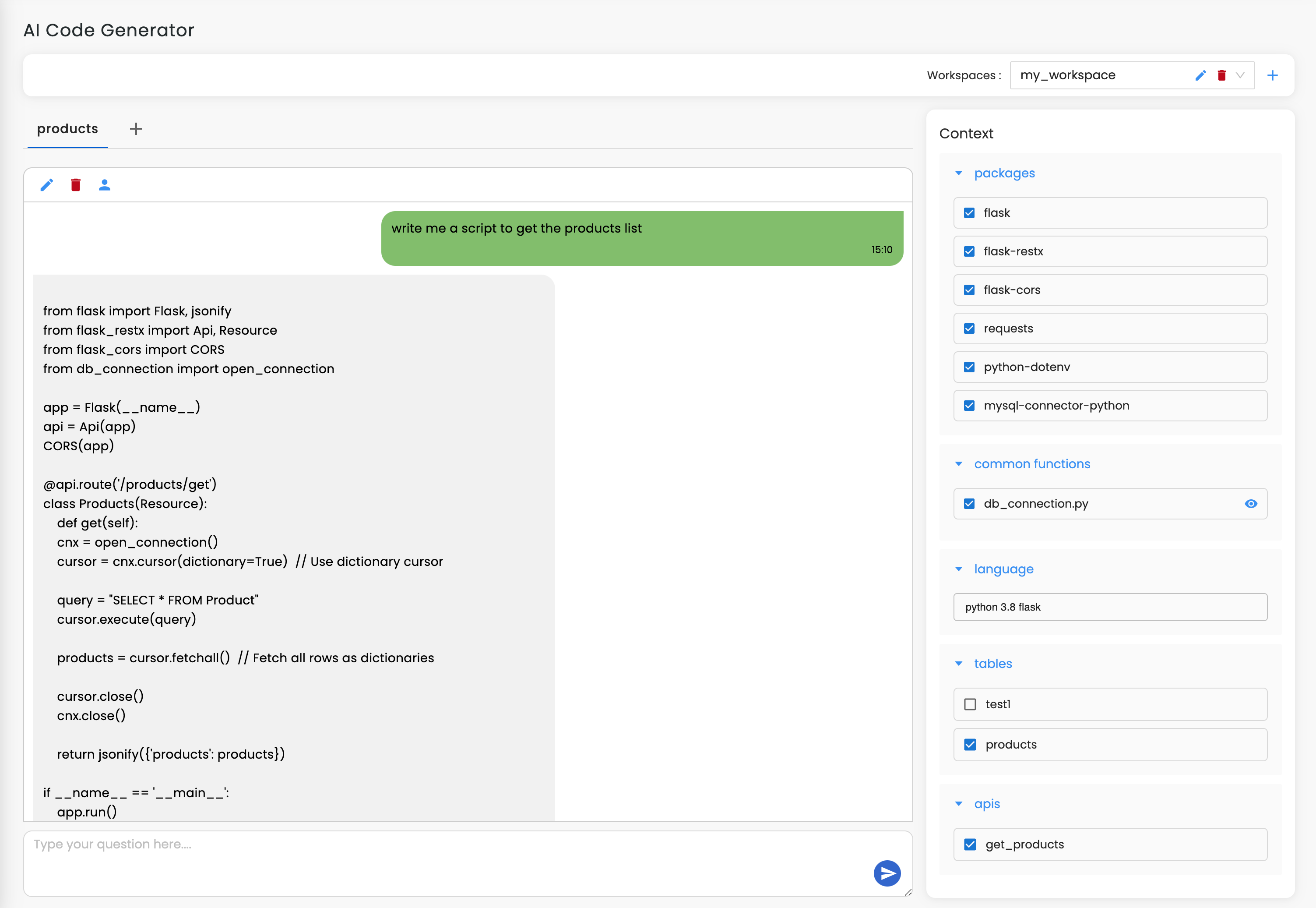
Access Database Tools or AI DB Documentation feature to upload your MS-SQL schema (JSON or CSV) or directly connect your database for documentation.
Use AI to auto-document MS-SQL tables, keys, constraints, stored procedures, indexes, and relationships. You can generate documentation manually or in bulk. Workik provides default layouts or helps you save your preferred layout for documentation.
Invite your team to share & refine documentation together. Run additional AI tasks like updates, comparisons, analysis, or schema-drift checks.
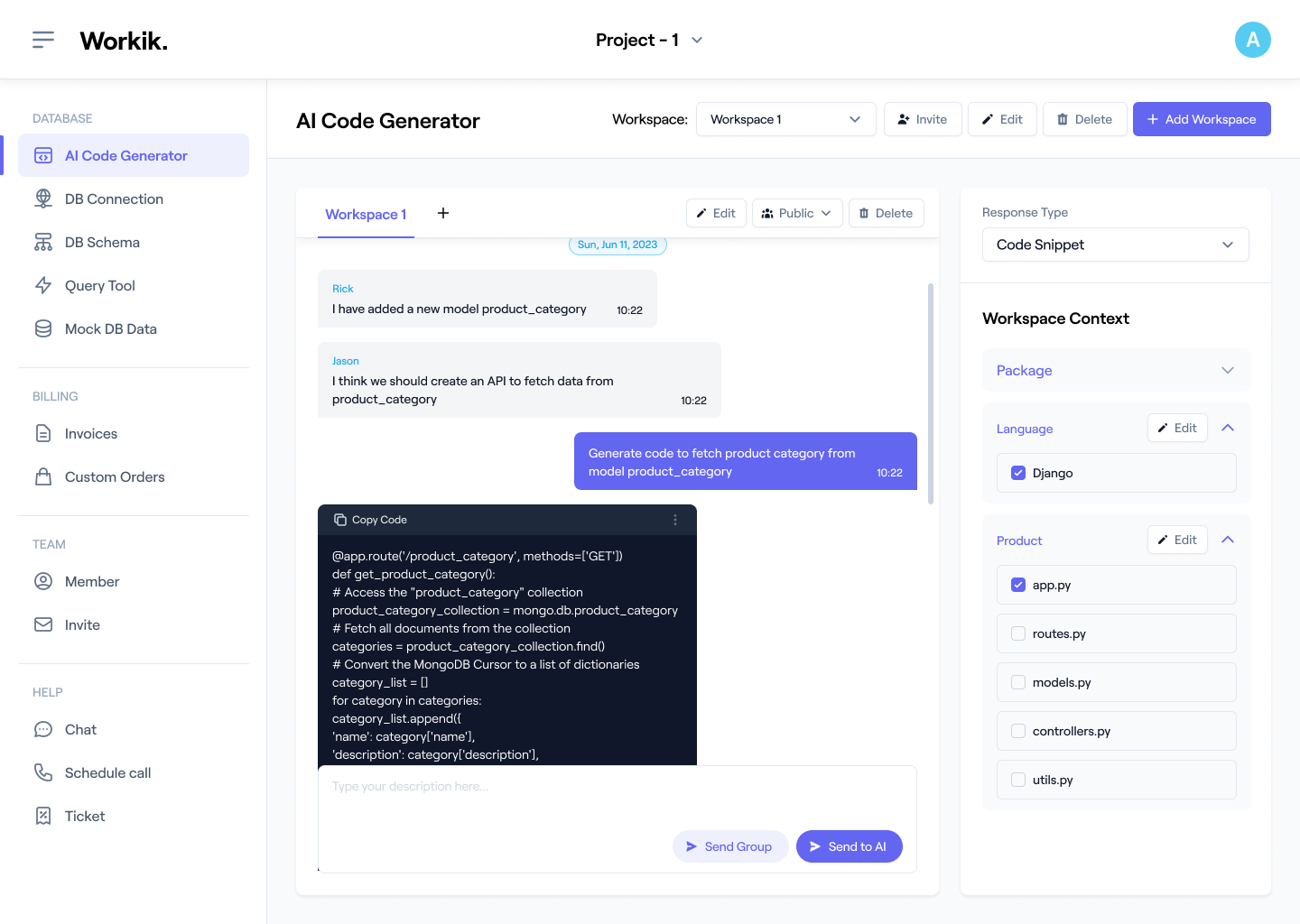

Expand
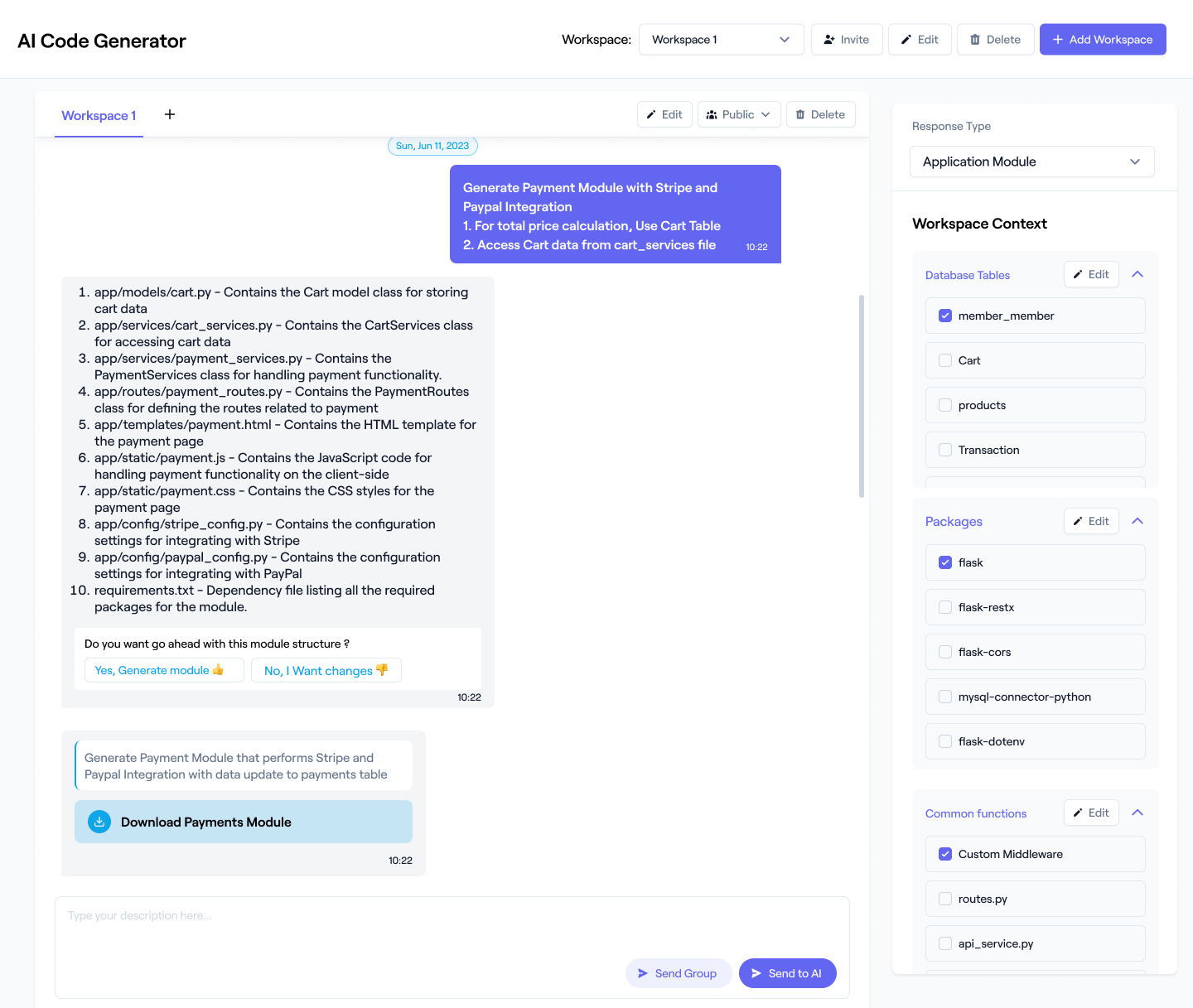

Expand
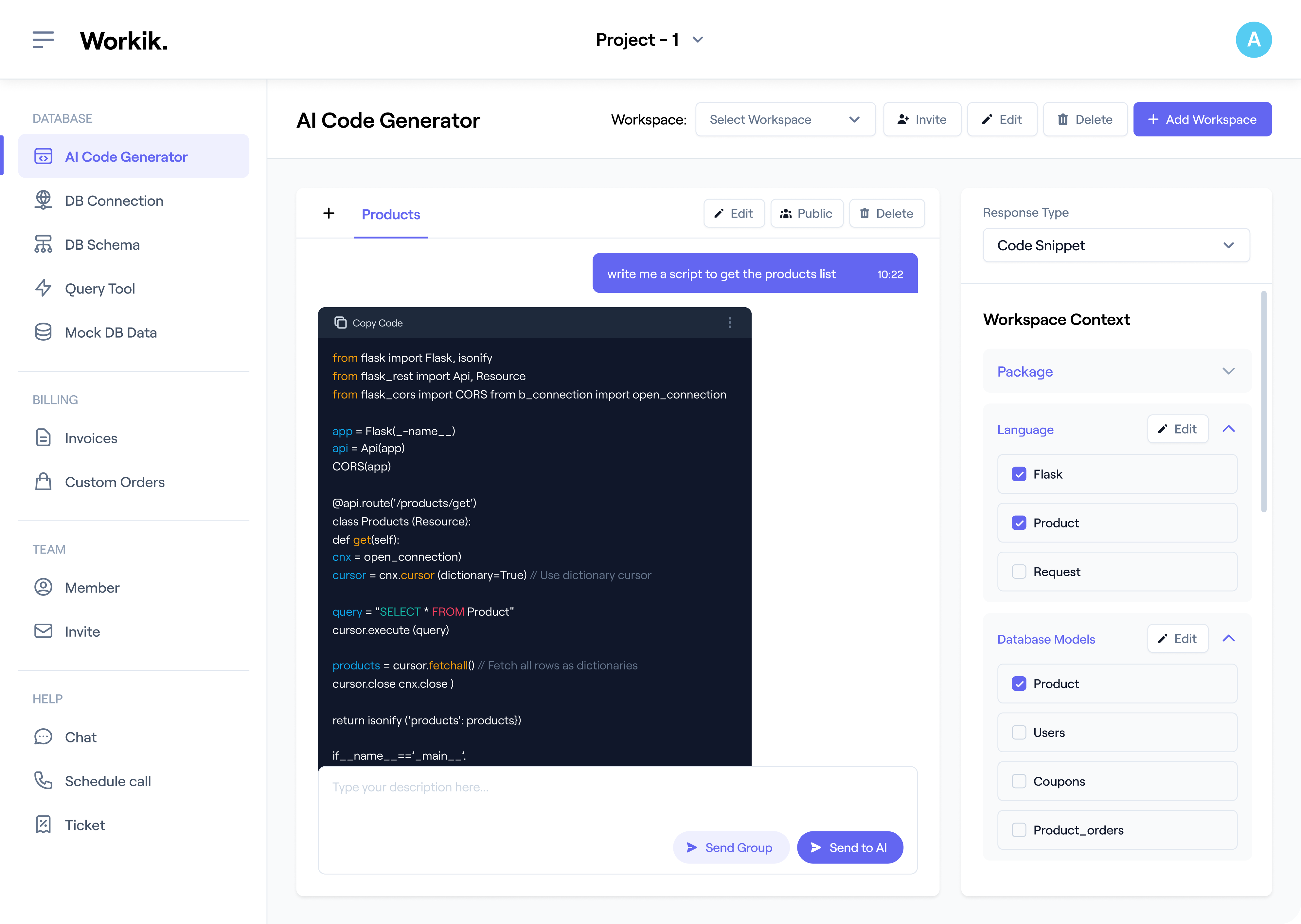

Expand
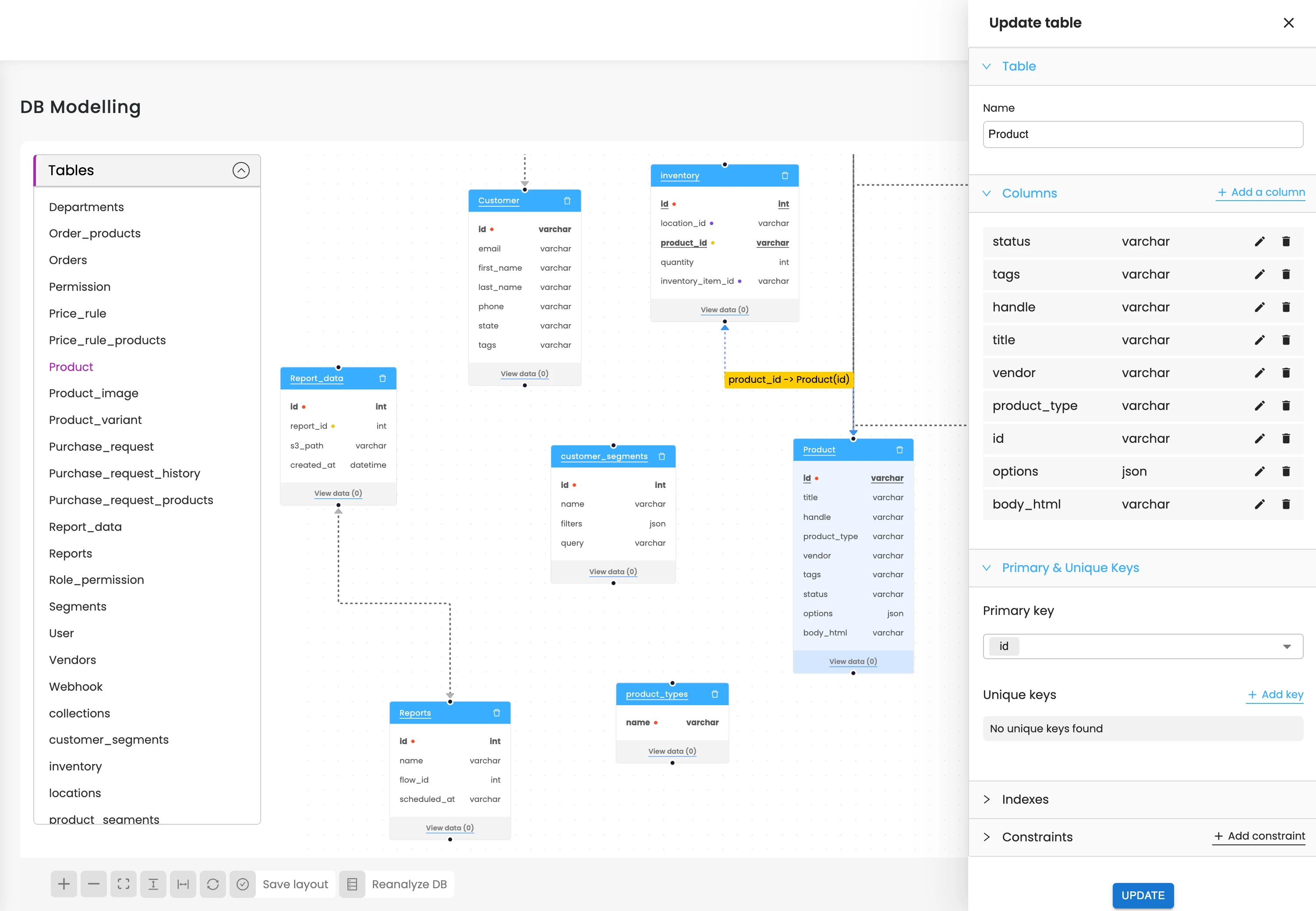

Expand

Expand


Expand


Expand


TESTIMONIALS
Real Stories, Real Results with Workik
"Our BI team relies on Workik AI to understand data lineage and view logic. It instantly clarified dependencies across our MS-SQL warehouse."
.png)
Marcus Fischer
Data Analyst
"The ability to upload a schema and get clean, well-structured documentation instantly boosted our API development speed."
.png)
Sarah Coleman
Backend API Developer
"We migrated an old MS-SQL system, and Workik AI produced the documentation that made sense. The AI summaries were spot-on."
.png)
Jared Kim
Software Architect
What are the most popular use cases for developers using Workik’s MS-SQL Database Documentation Generator?


Developers rely on Workik AI to understand, document, and analyze MS-SQL databases, including but not limited to:
* Auto-generate structured MS-SQL schema documentation for tables, columns, and constraints.
* Produce ERDs as AI maps foreign keys and inferred table relationships.
* Document stored procedures and functions with AI summarizing logic, parameters, and table references.
* Decode legacy MS-SQL systems where AI explains outdated structures and hidden dependencies.
* Identify migration gaps as AI flags unused tables, deprecated columns, and schema inconsistencies.
* Document indexing strategies as AI highlights key usage patterns and performance implications.
* Detects schema drift where AI compares environments and surfaces object-level differences.
* Speed up onboarding with AI summaries explaining core tables, business logic, and system behavior.
Is it necessary to connect an external database to generate MS-SQL documentation?


No, connecting a live MS-SQL database is optional. You can upload your schema in SQL, JSON, or CSV format and avoid sharing production access. Workik will generate full documentation, ERDs, stored logic insights, and relationship analysis directly from the uploaded schema without requiring a database connection.
Can AI document stored procedures, functions, and triggers with execution-flow awareness?


Absolutely. AI interprets procedure bodies, conditional branches, exception flows, table references, and return sets. This gives developers a readable breakdown of logic, helping them debug faster and understand how business rules are enforced within T-SQL.
How does the documentation generator handle MS-SQL relationships that aren’t defined through foreign keys?


AI can detect implicit relationships by examining naming patterns, join behaviors inside stored logic, and recurring usage patterns. Even if a foreign key is missing, AI can infer relationships like "Order.CustomerID references Customers.Id" and describe how objects interact in real-world queries.
Does Workik AI detect MS-SQL schema drift across environments?


Yes. AI compares schemas from dev, staging, and production to highlight discrepancies such as missing columns, changed datatypes, altered constraints, or version mismatches in stored procedures. This is particularly powerful for CI/CD pipelines, release reviews, and debugging deployment issues.
Can AI help document indexing strategies and their performance implications?


Yes. Instead of listing indexes, AI explains their purpose, usage patterns, and expected impact on queries. It highlights redundant indexes, unused keys, and potential performance bottlenecks, making it especially useful for tuning-heavy MS-SQL workloads.
Can MS-SQL documentation be regenerated as schemas evolve?


Yes. You can regenerate documentation whenever the schema changes. When tables, columns, constraints, indexes, or stored logic are updated, you trigger a fresh analysis so the documentation reflects the current MS-SQL structure and avoids drift after refactors or releases.
Generate Code For Free

MS-SQL Database Documentation Question & Answer
MS-SQL Database Documentation refers to the structured explanation of SQL Server database objects like tables, columns, keys, functions, stored procedures, triggers, indexes, views, schemas, and relationships. It provides clarity on data models, logic flow, dependencies, constraints, lineage, performance structures, and business rules embedded within T-SQL.
Popular frameworks, tools, and ecosystems used to generate or manage MS-SQL documentation include:
Documentation & Schema Tools:
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Azure Data Studio, Redgate SQL Doc, Dataedo, ER/Studio, SchemaSpy, dbdiagram.io / dbdocs.io.
ORM & Application Frameworks (Documentation-Related):
Entity Framework Core (EF Core), Dapper, ADO.NET, NHibernate, LINQ to SQL.
Metadata & Analysis Utilities:
SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT), SQL Server Profiler, sys.objects / sys.columns catalog views, Information Schema Views, Extended Properties / sp_addextendedproperty.
BI & Pipeline Documentation Tools:
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS), SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS).
Hosting & Versioning:
GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket (schema version control), Azure DevOps (database CI/CD).
Popular use cases include:
Schema Documentation:
Document tables, columns, datatypes, constraints, extended properties, and relationships across MS-SQL databases.
Stored Logic Documentation:
Document stored procedures, triggers, table-valued functions, scalar functions, and business rules embedded in T-SQL.
ERD & Relationship Mapping:
Generate visual relationship diagrams across tables, inferred relations, many-to-many bridges, and schema dependencies.
Legacy System Analysis:
Decode undocumented or partially maintained MS-SQL systems, mapping implicit relationships and outdated logic.
API & Integration Documentation:
Document database structures powering REST/GraphQL APIs, microservices, ETL workflows, and warehouse pipelines.
BI & Data Warehouse Understanding:
Explain fact/dimension models, SSIS pipelines, SSAS cubes, and reporting-layer transformations.
Performance & Index Documentation:
Describe indexing strategies, key lookups, partitioning behavior, constraints, and performance-relevant metadata.
Exception & Constraint Documentation:
Document check constraints, cascading rules, error-raising logic, and validation enforced at the database level.
Versioned Documentation:
Maintain documentation across branches, deployments, and environment lifecycle (dev → stage → prod).
Workik AI supports a wide range of MS-SQL Database Documentation tasks, including:
Schema Extraction & Documentation:
Automatically document tables, schemas, data types, keys, constraints, indexes, and extended properties.
Stored Logic Analysis:
Explain stored procedure flows, function logic, trigger operations, parameters, conditional branches, and referenced tables.
Automated ERD Generation:
Map foreign keys, inferred relationships, bridging tables, and dependency graphs across the entire MS-SQL ecosystem.
Legacy Database Interpretation:
Decode old MS-SQL systems by identifying implicit relationships, hidden dependencies, inconsistent naming, and undocumented logic.
API & Integration-Level Documentation:
Document structures powering backend services, integration endpoints, SSIS pipelines, and data movement workflows.
Warehouse & BI Documentation:
Generate documentation for fact/dim tables, staging layers, views, transformations, and lineage across analytic workloads.
Index & Performance Insight Extraction:
Summarize index behavior, key usage patterns, query hotspots, fragmentation risks, and optimization opportunities.
Refactoring & Migration Assistance:
Identify unused tables, deprecated columns, risky dependencies, schema anomalies, and modernization opportunities.
Drift & Version Control Documentation:
Track and document differences across dev, staging, and production schemas during deployments or migration cycles.
Testing & Validation Documentation:
Generate sample SQL queries, CRUD patterns, edge-case behaviors, and expected outputs to aid test planning.
Environment-Level Documentation:
Produce versioned documentation sets aligned with Git-based workflows for long-term maintainability.
Explore more on Workik
Top Blogs on Workik
Get in touch
Don't miss any updates of our product.
© Workik Inc. 2026 All rights reserved.

