Join our community to see how developers are using Workik AI everyday.
Supported AI models on Workik
GPT 5.2 Codex, GPT 5.2, GPT 5.1 Codex, GPT 5.1, GPT 5 Mini, GPT 5
Gemini 3.1 Pro, Gemini 3 Flash, Gemini 3 Pro, Gemini 2.5 Pro
Claude 4.6 sonnet, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, Claude 4.5 Haiku, Claude 4 Sonnet
Deepseek Reasoner, Deepseek Chat, Deepseek R1(High)
Grok 4.1 Fast, Grok 4, Grok Code Fast 1
Models availability might vary based on your plan on Workik
Features

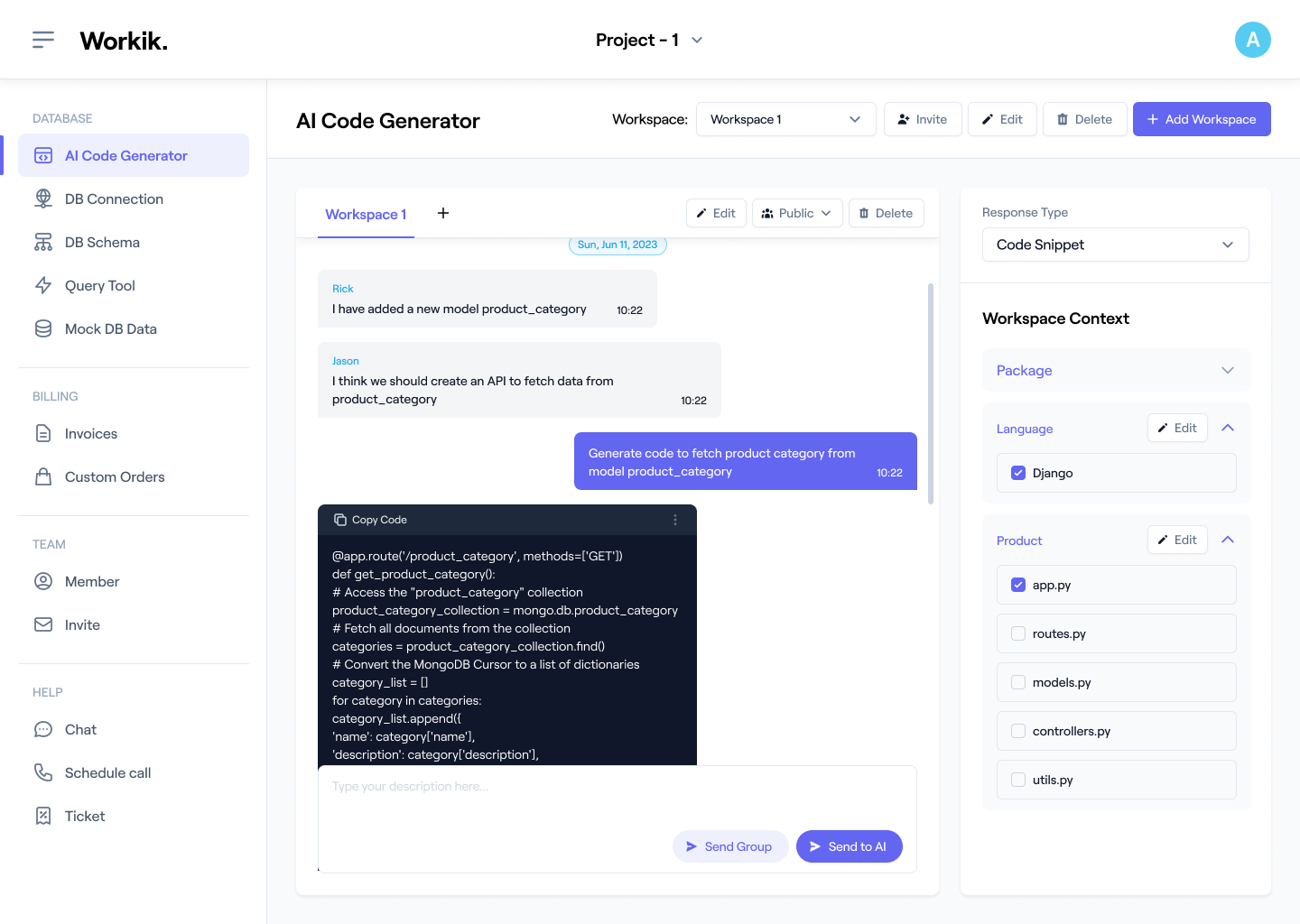
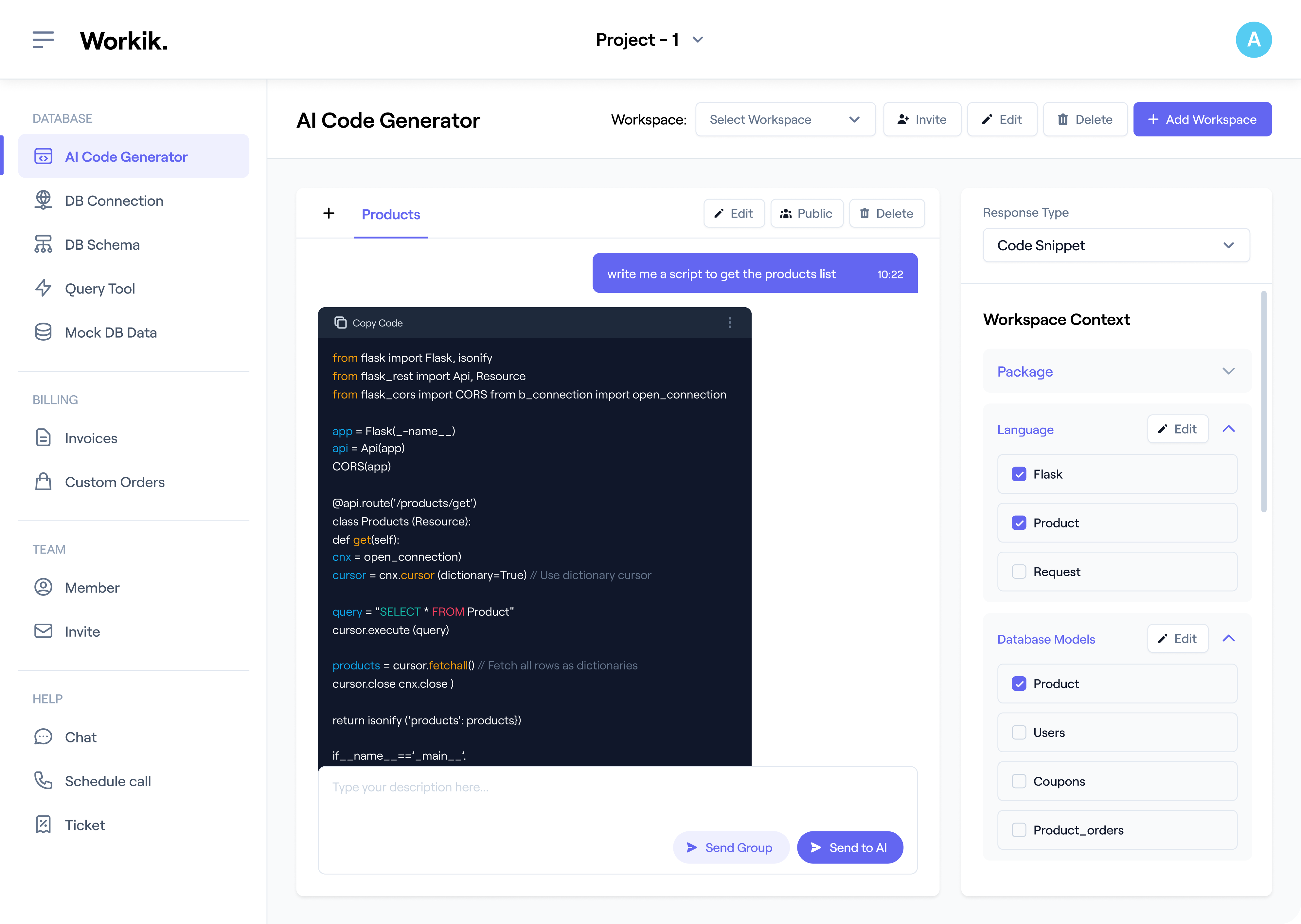
Parse Schema Instantly
AI interprets tables, columns, and constraints to deliver clean, accurate structured MariaDB documentation.

Map Relationships Clearly
Foreign keys and relational flows are identified by AI to clarify join paths and dependency chains.

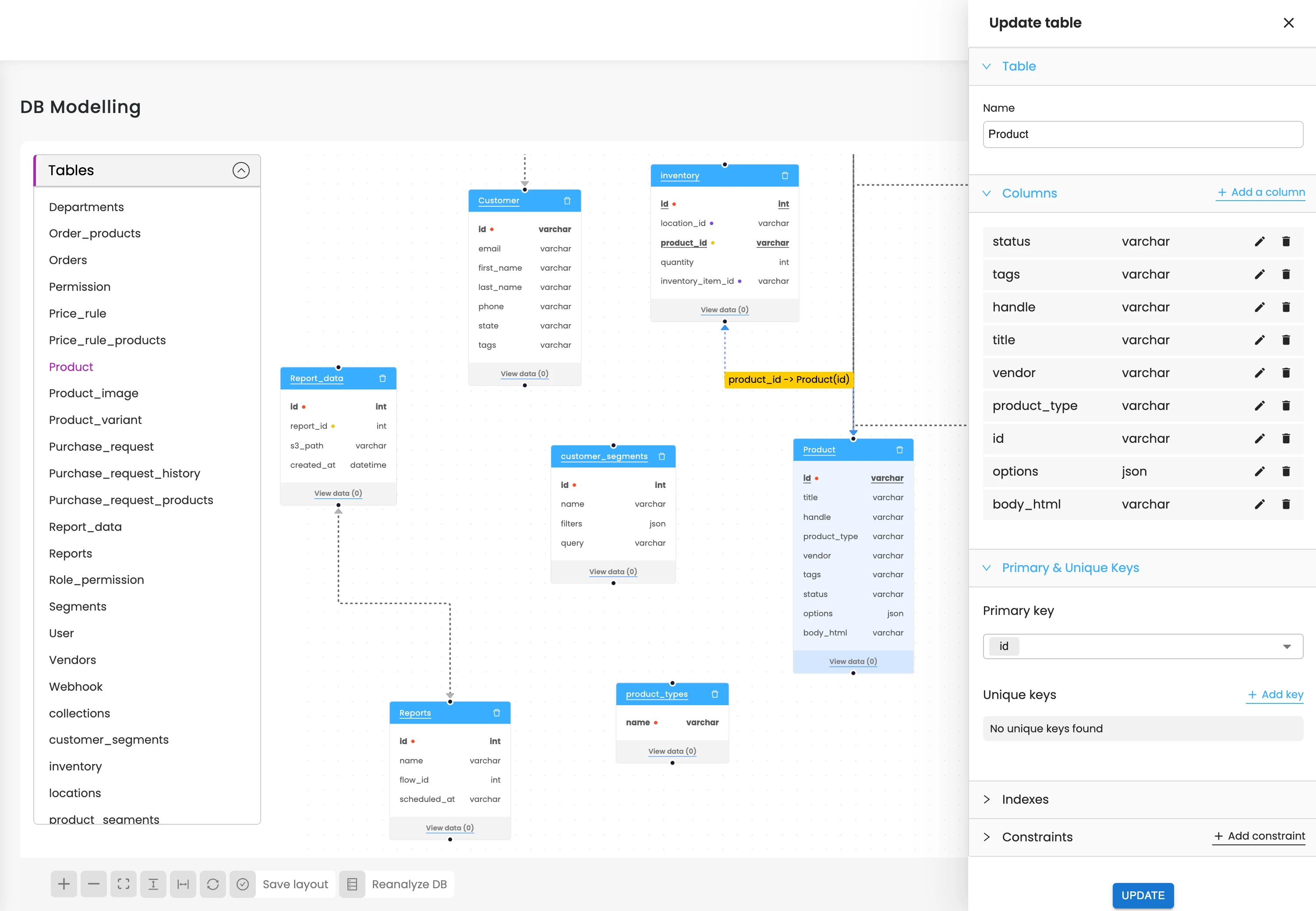
Generate ER Diagrams
ERDs are automatically built from your MariaDB schema, giving beginners clarity and experts quick architecture views.

Decode Legacy Schemas
AI transforms inherited or poorly documented MariaDB schemas into understandable documentation without relying on comments.
How it works
Create your free Workik account in seconds using Google or manually sign up. Start generating MariaDB documentation directly inside a clean, ready-to-use workspace.
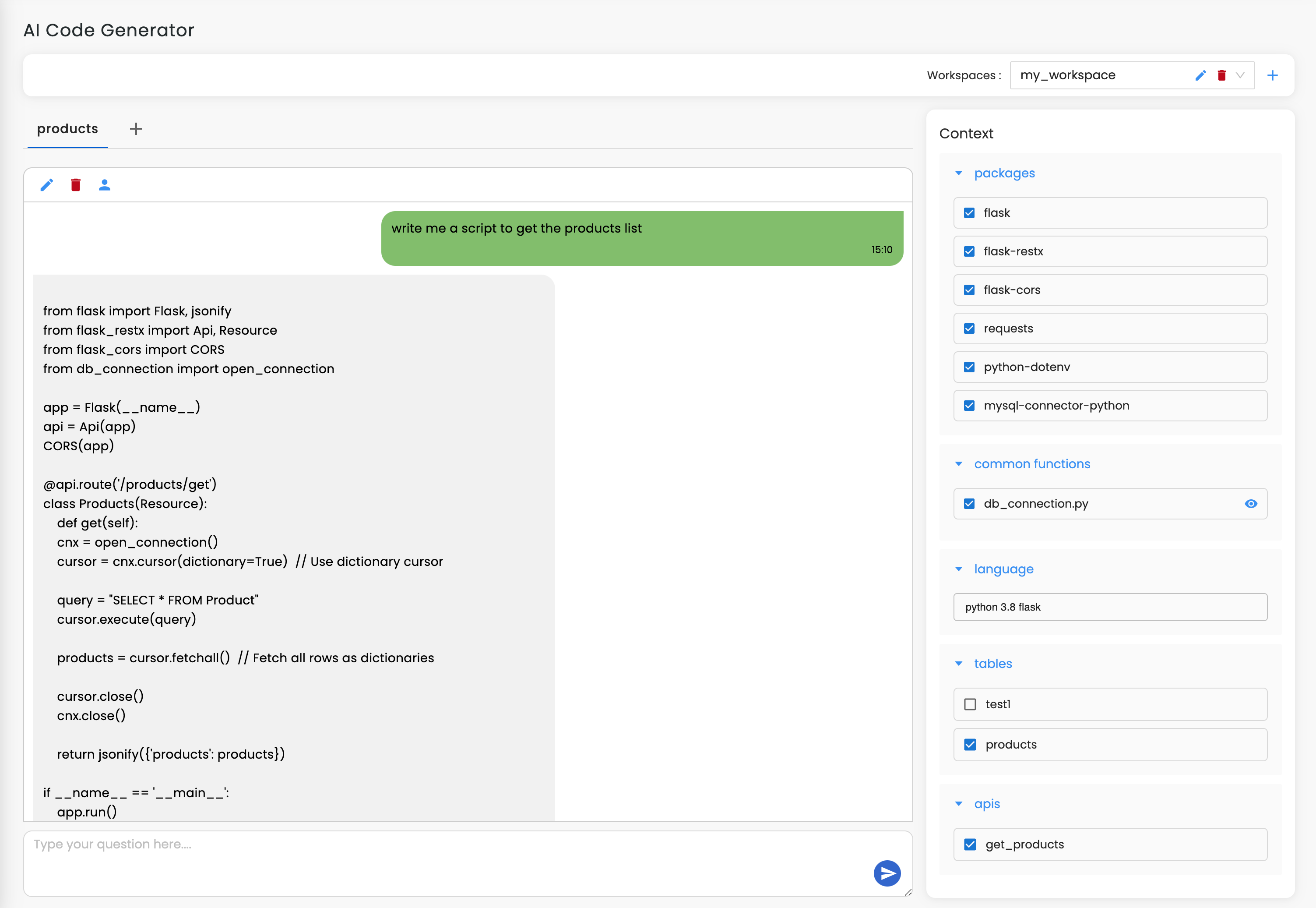
Get started from Database Tools or the DB Documentation feature. Upload your MariaDB schema or connect your database directly so Workik can understand your tables, relationships, and structure for precise AI-generated documentation.
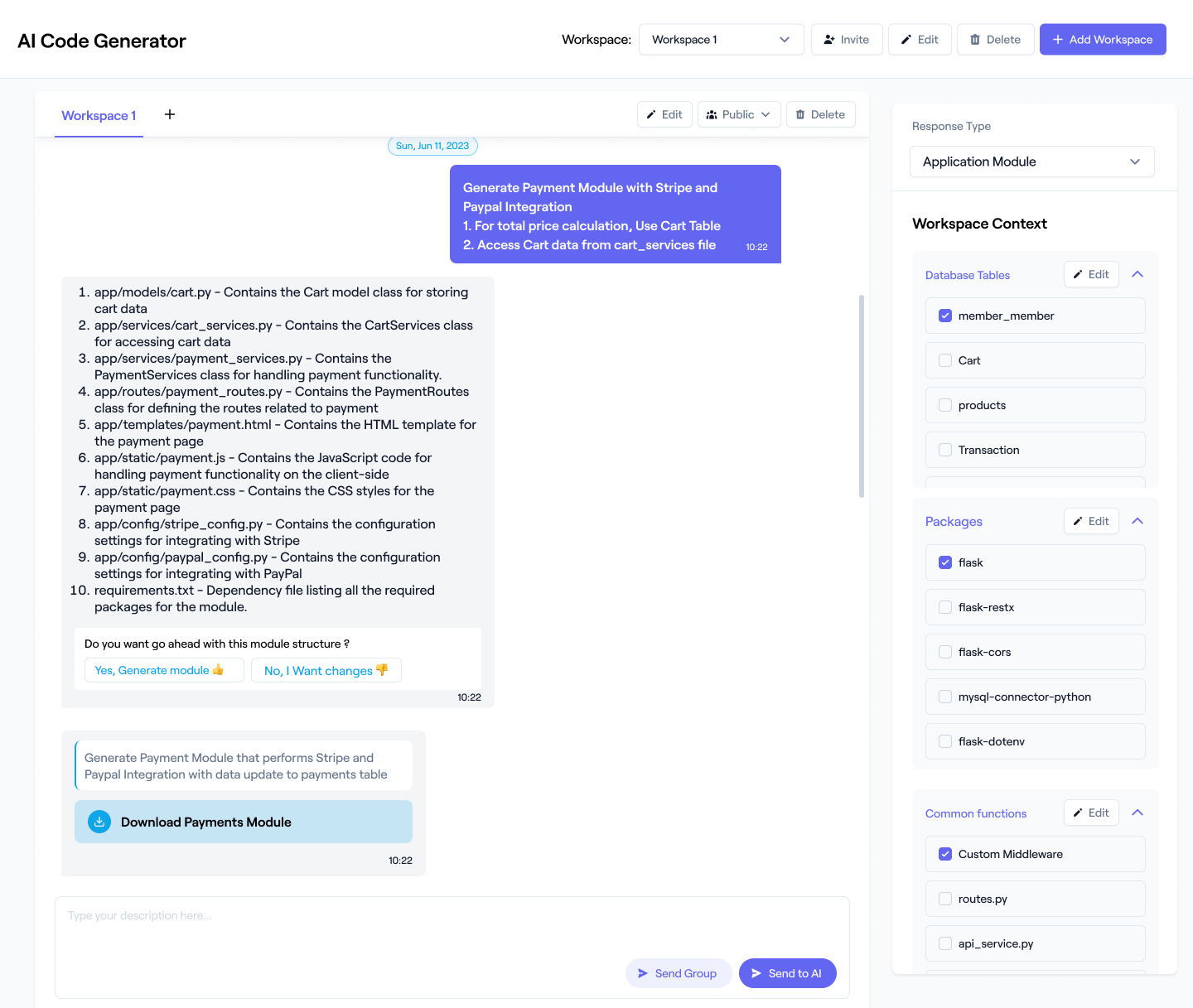
Ask AI to parse schemas, map relationships, generate ERDs, explain structures, or produce full MariaDB documentation tailored to your project’s architecture and workflows. Generate documentation manually or in bulk, apply default layouts, or save custom layouts for consistent MariaDB documentation.
Invite your team for shared documentation access. Expand your workflow using Workik’s automation, queries, mock data, and multi-workspace collaboration features.

Expand

Expand

Expand

Expand

Expand


Expand


Expand


TESTIMONIALS
Real Stories, Real Results with Workik
"As a DBA, I rely on Workik AI to map relationships and constraints instantly. The AI-generated ERDs have saved me hours on every schema review."
.png)
Victor Ramirez
Database Administrator
"Our API team now understands table structures without deciphering SQL dumps. Workik’s documentation made cross-team collaboration with MariaDB effortless."
.png)
Karthik Ganesan
Full-Stack Developer
"Testing became faster after Workik AI clarified our MariaDB relationships. The documentation exposed edge-case flows I wouldn’t have caught manually."
.png)
Rebecca Keller
QA Automation Lead
What are the most common use cases for developers using Workik AI MariaDB Database Documentation Generator?


Developers rely on AI to streamline MariaDB documentation workflows, including but not limited to:
* Generating complete schema documentation from raw database structures.
* Auto-building ER diagrams to visualize complex table relationships.
* Explaining foreign key links and join paths for safer query design.
* Documenting triggers, procedures, and functions with readable AI summaries.
* Identifying inconsistencies like mismatched data types or missing constraints.
* Producing onboarding-friendly schema overviews for new team members.
* Highlighting index usage patterns to support query performance tuning.
* Detecting risky schema patterns like nullable keys or unused tables.
* Clarifying where sensitive or regulated data is stored for compliance.
* Mapping relationships across multiple MariaDB databases in distributed systems.
* Describing each table’s purpose within the application's data flow.
* Converting legacy stored logic into modern, understandable explanations.
Is it necessary to connect an external database to generate MariaDB documentation?


No, connecting a live database is optional. You can simply upload your MariaDB schema in SQL, JSON, or CSV format. Workik’s AI will generate full documentation, ER diagrams, relationship mappings, and structural insights directly from the uploaded schema without needing direct database access.
How does Workik AI understand complex or legacy MariaDB schemas?


Workik AI analyzes foreign keys, composite keys, bridge tables, indexes, triggers, and stored logic to build a complete structural view of the schema. In legacy or inconsistent databases where constraints may be missing, it also infers relationships from naming conventions and usage patterns to provide useful context. This allows teams to understand complex, long-lived MariaDB schemas without relying on outdated documentation or tribal knowledge.
What types of MariaDB structures can AI document beyond tables and columns?


AI documents triggers, stored procedures, functions, views, events, indexes, and constraints. It includes execution context, behavioral notes, and how each of these interacts with underlying tables, such as highlighting triggers that enforce soft deletes or procedures that manage financial calculations.
Can AI help explain stored logic and business rules embedded inside the MariaDB database?


Yes. AI generates human-readable explanations for complex DB-side logic. It breaks down conditional flows, update paths, and dependencies. For example, “This trigger logs every price change to product_history for audit purposes.” This is invaluable for developers inheriting systems with undocumented business logic.
Can AI-generated MariaDB documentation flag data integrity risks or model inconsistencies?


Yes. AI detects gaps such as missing foreign keys, mismatched data types across related columns, nullable fields in critical relationships, duplicated data flows, and unindexed join paths. These insights help prevent production bugs, logic conflicts, and data corruption.
How does AI help teams preparing for MariaDB migrations or schema refactoring?


AI highlights high-risk dependencies, cascade behaviors, relational bottlenecks, and tight coupling between tables. For example, if changing a primary key in users affects sessions, orders, or billing, AI surfaces those relationships to guide safer planning, testing, and migration rollout.
How does MariaDB documentation stay accurate as schemas change?


MariaDB documentation can be regenerated whenever the schema evolves. As tables, columns, relationships, indexes, or stored logic are added or modified, users can regenerate documentation to reflect the latest structure and dependencies. This prevents documentation drift after migrations, refactors, or feature releases and ensures the documentation remains aligned with the actual database state over time.
Generate Code For Free

MariaDB Database Documentation Question & Answer
MariaDB Database Documentation refers to the structured explanation of a MariaDB database’s schema, tables, columns, constraints, relationships, indexes, stored logic, and data flow. This includes entity-relationship details, foreign key paths, table purposes, data types, triggers, stored procedures, views, and operational behavior.
Popular frameworks, tools, and technologies for documenting MariaDB databases include:
Schema & Documentation Generators:
SchemaSpy, DbSchema, Dataedo, DBeaver Docs, MySQL Workbench (MariaDB compatible), dbdocs.io.
ER Diagram & Modeling Tools:
Draw.io, Lucidchart, ERDPlus, TablePlus, JetBrains DataGrip.
Linting, Validation & Analysis Utilities:
MariaDB Information Schema tools, SQLFluff, MySQLShell utilities, SchemaCrawler.
ORM & Framework Auto-Docs:
Laravel Eloquent, Django ORM, SQLAlchemy, Hibernate, Sequelize, TypeORM.
API & Integration Documentation:
Swagger/OpenAPI for DB-backed API structures, Postman Collections for documenting query-based workflows.
Publishing & Collaboration:
Confluence, GitHub Pages, Read the Docs (for mixed code + database docs), Notion technical documentation spaces.
Popular use cases include:
Schema Documentation:
Document tables, columns, data types, primary keys, foreign keys, indexes, constraints, and table-level descriptions.
ER Diagram Generation:
Produce entity-relationship diagrams to visualize joins, relationships, bridge tables, and cardinality across the database.
Stored Logic Documentation:
Explain stored procedures, triggers, functions, events, and how they interact with underlying tables.
API & Integration Understanding:
Map how backend services, ORMs, GraphQL layers, or REST APIs interact with MariaDB tables and queries.
Data Flow Documentation:
Show how data moves between tables (e.g., order → order_items → payments), or across microservices using multiple MariaDB instances.
Performance & Index Documentation:
Document indexing strategies, usage patterns, and query performance considerations for optimization.
Refactoring & Migration Support:
Document schema changes for safe refactoring, MySQL-to-MariaDB migrations, or versioned database updates.
Onboarding & Knowledge Sharing:
Provide clear, structured documentation so new developers understand database architecture without reverse-engineering SQL.
Risk & Integrity Documentation:
Highlight nullable critical fields, mismatched data types, denormalized structures, or missing constraints.
Version-Controlled Documentation:
Maintain documentation across branches or releases for teams using Git-based workflows or frequent schema updates.
Workik AI supports a wide range of MariaDB documentation workflows, including:
Schema Interpretation:
Automatically read your MariaDB schema (via upload or DB connection) and generate structured documentation of tables, columns, constraints, and relationships.
ERD & Relationship Mapping:
Generate ER diagrams, identify foreign key paths, detect join tables, and map many-to-many relationships with clarity.
Stored Logic Analysis:
Document triggers, stored procedures, events, and functions with AI-generated explanations of execution flow and table dependencies.
Table Role Classification:
Identify reference tables, transactional tables, junction tables, logs, and historization tables for clearer domain understanding.
Performance Context Documentation:
Highlight index usage, potential full-table scans, and schema areas that may affect query performance or scalability.
Data Integrity & Constraint Insight:
Flag nullable critical fields, mismatched data types, missing relationships, and weak constraint structures.
Refactoring & Migration Intelligence:
Generate documentation to assist with schema consolidation, normalization/denormalization, or service extraction in microservice migrations.
Cross-Service Schema Documentation:
Document multiple MariaDB databases in distributed applications and map interactions or shared dependencies.
Test Planning & Validation Notes:
Produce example scenarios, key relationship notes, and structural behaviors that assist testing teams during integration or API validation.
Version-Specific Documentation:
Maintain versioned database documentation across branches or releases and track schema evolution using uploaded migration snapshots.
Explore more on Workik
Top Blogs on Workik
Get in touch
Don't miss any updates of our product.
© Workik Inc. 2026 All rights reserved.

