Join our community to see how developers are using Workik AI everyday.
Features

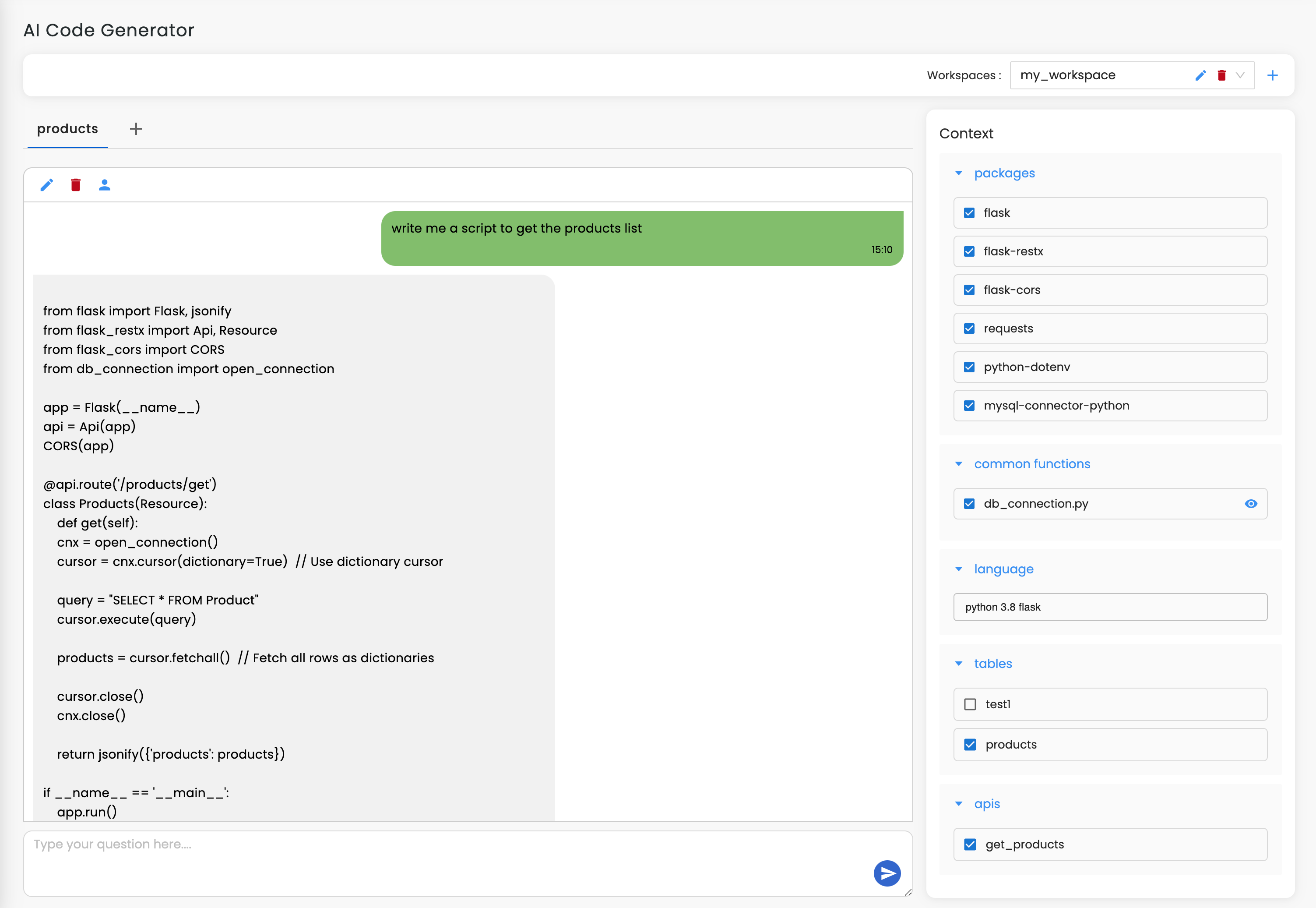
Streamline OTP System
AI generates OTP code for gen_server and supervision trees, enabling fault-tolerant, concurrent systems.

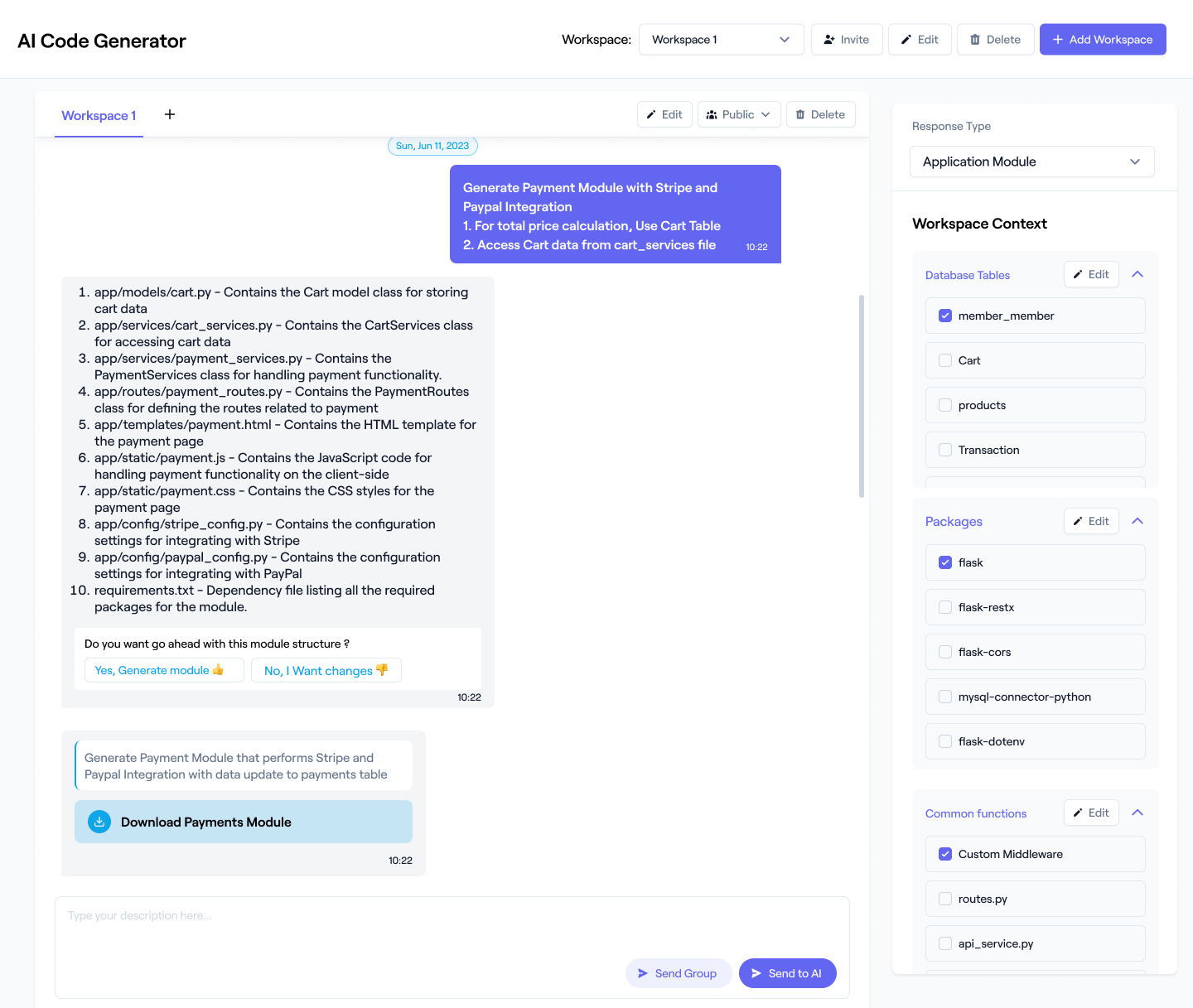
Seamless Distributed Messaging
Use AI to generate Erlang code for RabbitMQ or pg2, optimizing concurrency for scalable messaging across nodes.

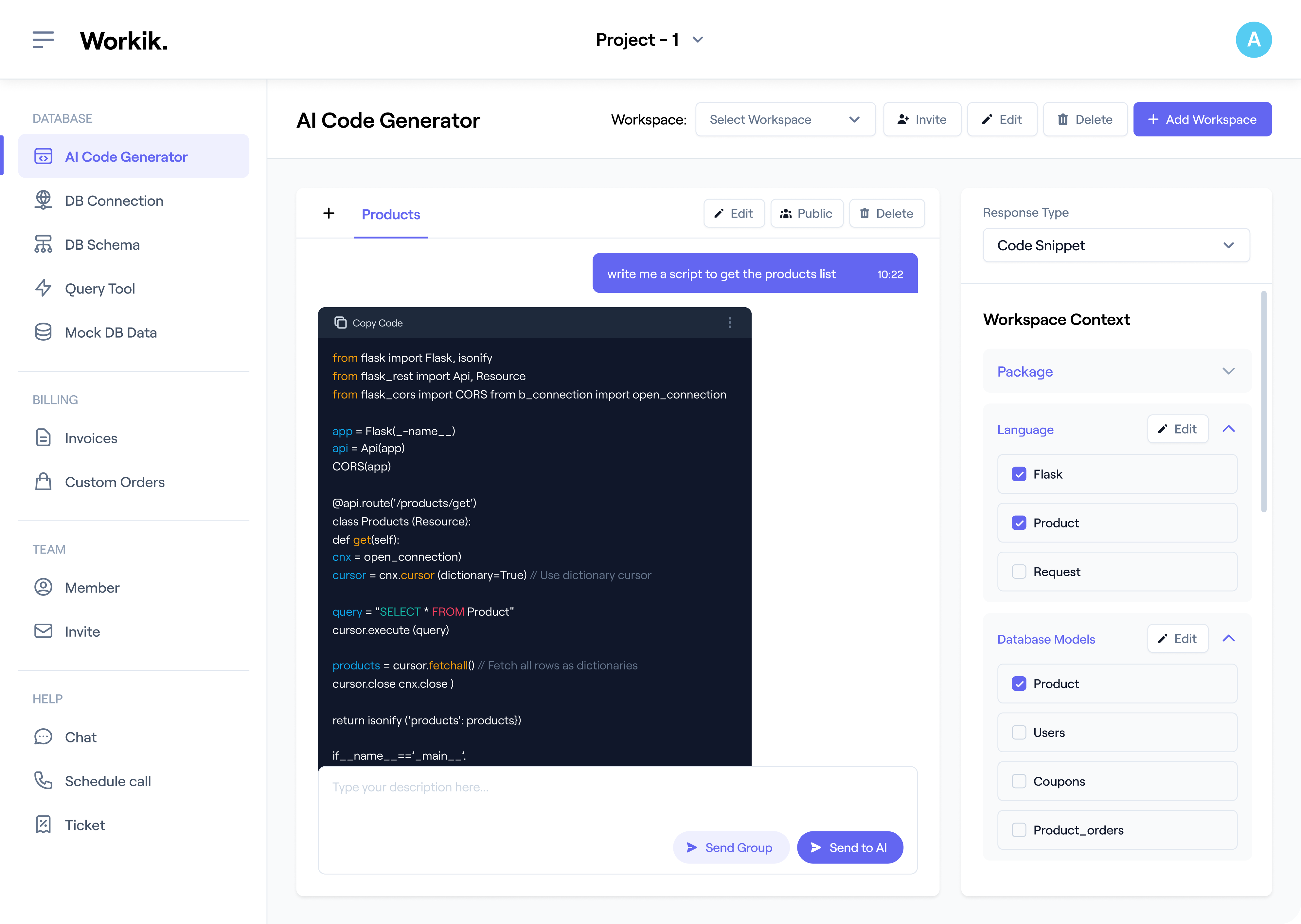
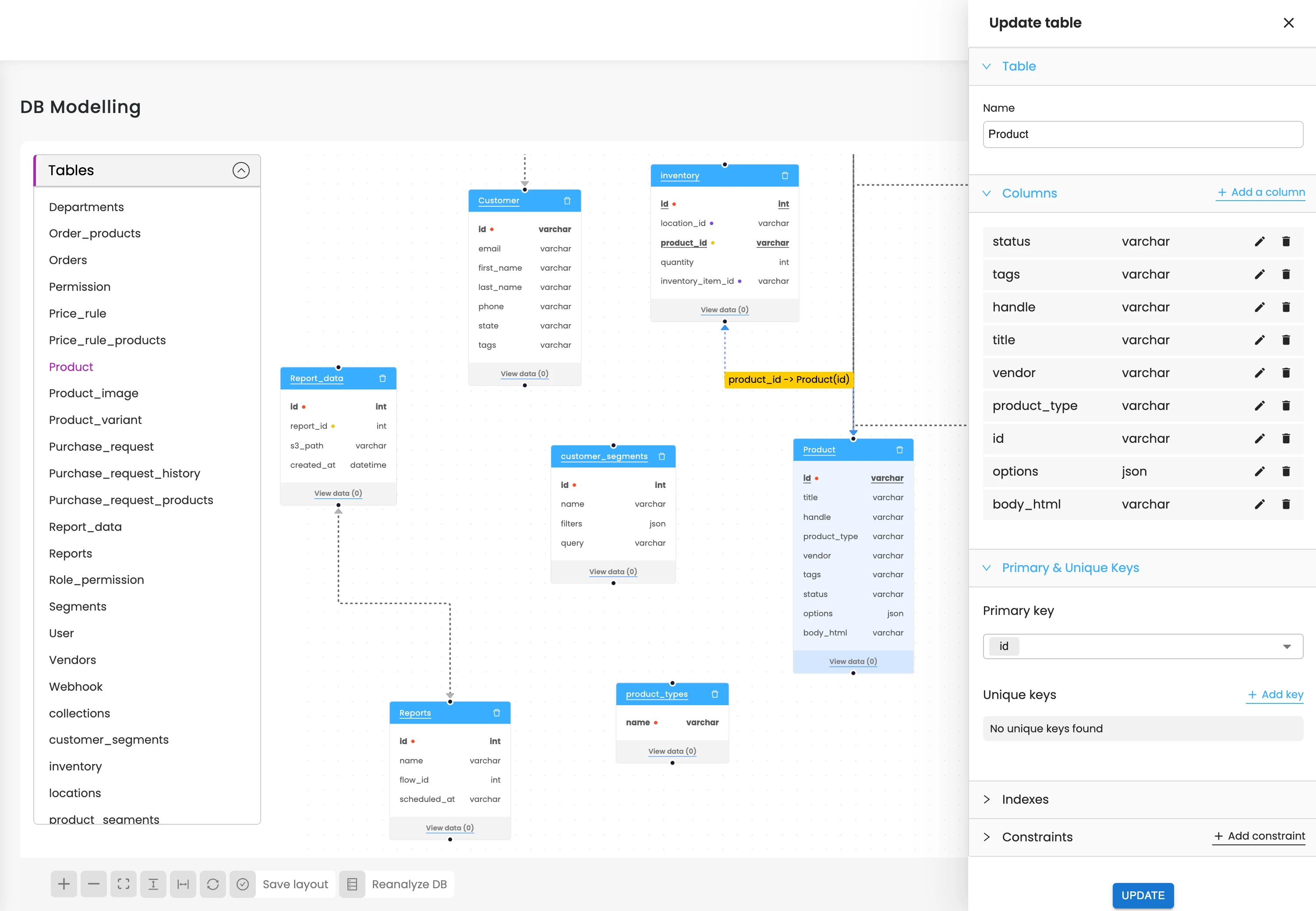
Optimize Database Performance
AI can refine Mnesia queries, boosting storage, retrieval speed, and schema efficiency.

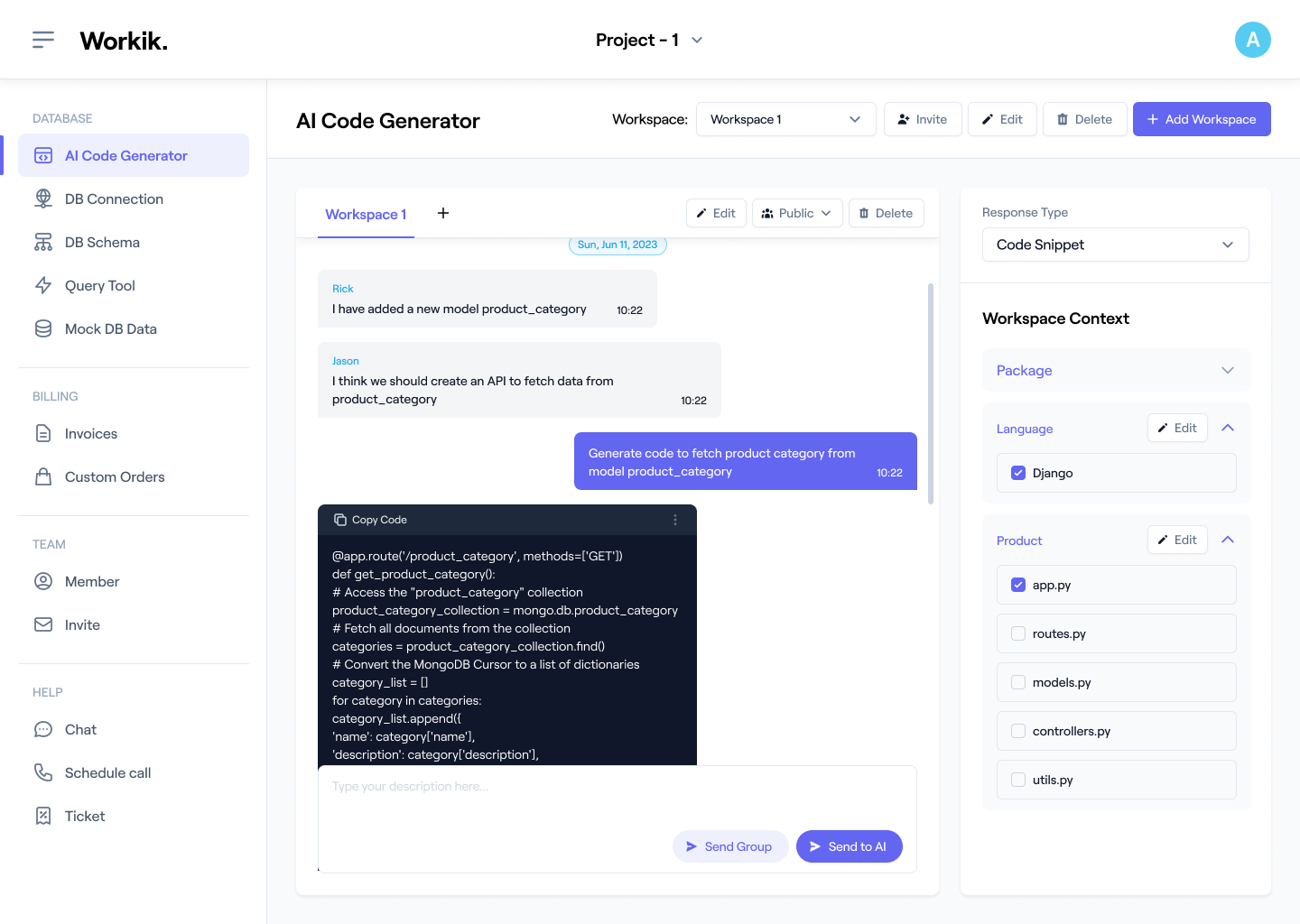
Generate and Test Web APIs
AI helps to create Erlang-based RESTful APIs with Cowboy or Yaws, generating unit and integration tests.
How it works
Sign up at Workik using your Google account or manually enter your details to kickstart your Erlang development.
Import your Erlang projects from GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. Define modules, functions, and services, and specify frameworks like OTP, Cowboy, or RabbitMQ for accurate AI guidance.
Leverage AI to generate Erlang code for processes, messaging, and databases. Automate debugging and testing, while AI optimizes concurrency, fault recovery, and ensures your system is robust and scalable.
Collaborate with your team in real-time using AI insights and deploy your Erlang applications. Easily manage distributed nodes and scale your system efficiently.

Expand

Expand

Expand

Expand

Expand


Expand


Expand


TESTIMONIALS
Real Stories, Real Results with Workik
Workik AI helps handle real-time messaging systems perfectly, generating efficient Erlang code instantly.

Benjamin Fisher
Systems Developer
We Generated highly scalable Erlang functions for telecom applications. Workik AI is a must-have for Erlang!

Maria Roberts
Telecom Developer
Workik AI generated complex Erlang modules for my distributed systems projects, cutting down coding time drastically.

Ravi Khanna
Software Engineer
What are some popular use cases of Workik's AI for Erlang code generation?


Popular use cases of Workik's AI for Erlang development include:
* Generate gen_server modules and supervision trees for fault-tolerant systems.
* Create distributed messaging architectures using RabbitMQ or pg2 for node communication and message routing.
* Optimize Mnesia database queries for high availability and efficient data replication across nodes.
* Generate RESTful APIs with Cowboy or Yaws, and automate the creation of unit and integration tests.
* Develop real-time applications using Erlang’s concurrency model for handling thousands of lightweight processes.
What are the context-setting options available on the Erlang Code Generator?


You can add the following context-setting options to Workik's Erlang Code Generator:
* Connect to GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket to sync your repository.
* Specify Erlang libraries and frameworks (e.g., OTP, Cowboy, Ranch).
* Provide database schemas for relational or NoSQL databases (e.g., PostgreSQL, Riak).
* Include API blueprints for microservices (e.g., Swagger or OpenAPI).
* Upload Erlang modules, distributed systems logic, or message-passing patterns.
* Add dynamic environment variables or configurations for concurrent processes.
* Include code snippets like gen_server or gen_fsm behavior patterns.
Does Workik AI assist with process supervision and recovery in distributed Erlang applications?


Workik AI generates supervision trees for Erlang applications, automating fault-tolerant process setups. This allows automatic recovery from failures, ensuring system resilience and uptime even during network issues or node failures.
Can Workik AI handle scalability challenges in Erlang applications?


Workik AI generates code optimized for distributed messaging and process concurrency, automating load balancing and node clustering to ensure smooth scalability across multiple nodes.
How does Workik AI optimize distributed node communication in Erlang?


Workik AI optimizes node-to-node communication in distributed Erlang systems, ensuring efficient message routing, reduced latency, and fault-tolerant messaging.
How does Workik AI assist in debugging complex Erlang applications?


Workik AI automates debugging in Erlang by identifying concurrency and messaging bottlenecks, analyzing crashes, and offering real-time fixes for deadlocks or failed message deliveries.
Can Workik AI help enhance security in Erlang applications?


Workik AI generates secure Erlang code by automating encryption for message passing, implementing secure authentication, and generating APIs that adhere to best security practices.
How can Workik AI assist with building telecom applications in Erlang?


Workik AI generates Erlang code for telecom applications, optimizing real-time call routing, message passing, and process management. It automates gen_server modules and supervision trees to ensure seamless communication and high availability for millions of connections.
Generate Code For Free

Erlang: Question and Answer
Erlang is a functional, concurrent programming language designed for building distributed, fault-tolerant systems. Erlang’s unique features include lightweight process handling, built-in support for concurrency, and fault tolerance, making it ideal for applications where system uptime and reliability are critical.
Popular frameworks and libraries used in Erlang development include:
Concurrency and Fault Tolerance:
OTP (Open Telecom Platform), gen_server, supervision trees
Messaging:
RabbitMQ, pg2
Web Servers:
Cowboy, Yaws
Data Persistence:
Mnesia
Testing:
EUnit, Common Test
Worker Pool Management:
Poolboy
Process Registry:
Gproc
Build Tools:
Rebar3
Popular use cases of Erlang include:
Telecom Systems:
Erlang’s fault tolerance and concurrency make it ideal for managing telecom systems, such as call routing and messaging.
Distributed Systems:
Handle large-scale, multi-node distributed systems with real-time message passing.
Real-Time Applications:
Develop real-time applications like chat servers, IoT systems, and event-driven architectures.
Microservices Architectures:
Build scalable microservices with independent fault-tolerant processes.
Messaging Systems:
Erlang powers RabbitMQ, a widely-used messaging broker for asynchronous messaging.
Database-Driven Applications:
Develop high-availability, distributed databases using Mnesia for real-time data replication and access.
Career opportunities and technical roles available for Erlang professionals include Telecom Systems Engineer, Distributed Systems Developer, Backend Engineer (Real-Time Applications), Microservices Architect, Messaging System Specialist, and Database Architect. Erlang developers are often sought in industries such as telecom, IoT, and FinTech.
Workik AI provides extensive Erlang development support, including:
1. Code Generation:
Automates code generation for OTP behaviors (gen_server, supervision trees), messaging architectures, and APIs with Cowboy or Yaws.
2. Debugging:
Identifies issues related to process crashes, concurrency bottlenecks, and message delivery in distributed systems.
3. Fault Tolerance:
Automates setup for fault-tolerant processes and supervision trees, ensuring system recovery from failures without downtime.
4. Performance Optimization:
Suggests improvements in process concurrency, load balancing, and optimizing Mnesia queries for efficient data handling.
5. Unit Testing:
Automates the generation of unit and integration tests using EUnit or Common Test to ensure system reliability.
6. Deployment:
Assists with multi-node deployment and scaling of distributed Erlang systems by automating node setup and configuration files.
7. Database Management:
Helps in setting up and optimizing Mnesia for real-time data replication and high-availability setups.
Explore more on Workik
Get in touch
Don't miss any updates of our product.
© Workik Inc. 2026 All rights reserved.

